https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/st/Decibels.html
A decibel (abbreviated dB) is defined as one tenth of a bel.
The bel is an amplitude unit
defined for sound as the log (base 10) of the intensity
relative to some reference intensity,
i.e.,
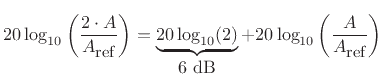
The choice of reference intensity (or power) defines the particular choice of dB scale. Signal intensity, power, and energy are always proportional to the square of the signal amplitude. Thus, we can always translate these energy-related measures into squared amplitude:
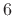
Since there are 10 decibels to a bel, we also have
In every kind of dB, a factor of 10 in amplitude increase corresponds
to a 20 dB boost (increase by 20 dB):


A function  which is
proportional to
which is
proportional to 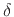 is said to ``fall off'' (or ``roll off'') at the
rate of
is said to ``fall off'' (or ``roll off'') at the
rate of 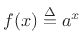 dB per decade. That is, for every factor of
dB per decade. That is, for every factor of 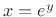 in
in 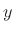 (every ``decade''), the amplitude drops
(every ``decade''), the amplitude drops 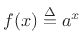 dB.
dB.
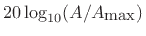
A function 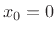 which is proportional to
which is proportional to 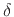 is said to fall off
is said to fall off
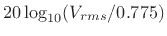 dB per octave. That is, for every factor of
dB per octave. That is, for every factor of 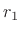 in
in 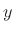 (every ``octave''), the amplitude drops close to
(every ``octave''), the amplitude drops close to 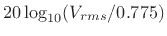 dB. Thus, 6 dB
per octave is the same thing as 20 dB per decade.
dB. Thus, 6 dB
per octave is the same thing as 20 dB per decade.
